What is the difference between dolomite and limestone?
What is the difference between dolomite and limestone?
Blog Article

Both dolomite and limestone are common building and industrial materials, but they have obvious differences in chemical composition, physical properties and uses. New Gaonai Heavy Industry will introduce the differences between dolomite and limestone in detail so that readers can better understand their characteristics and applications.
Different causes and distribution
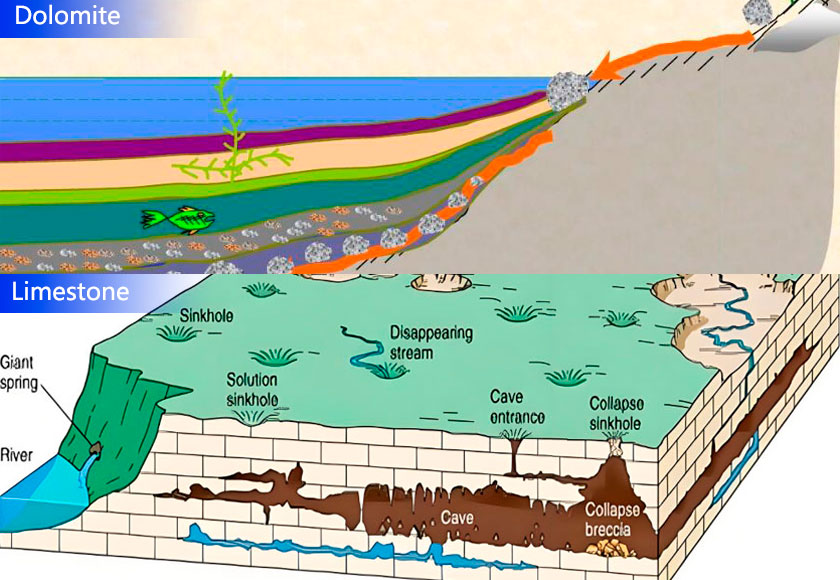
Dolomite: Mainly formed in regional metamorphism, contact metamorphism, hydrothermal alteration and sedimentation. Widely distributed, but the specific distribution is controlled by geological structure and sedimentary environment.
Limestone: It is composed of a variety of components such as physical changes of calcareous mud and decayed fragments of plants and animals, as well as organic compounds in seawater, which eventually form limestone. Widely distributed, especially in marine sediments and lake sediments.
Different colors and appearances
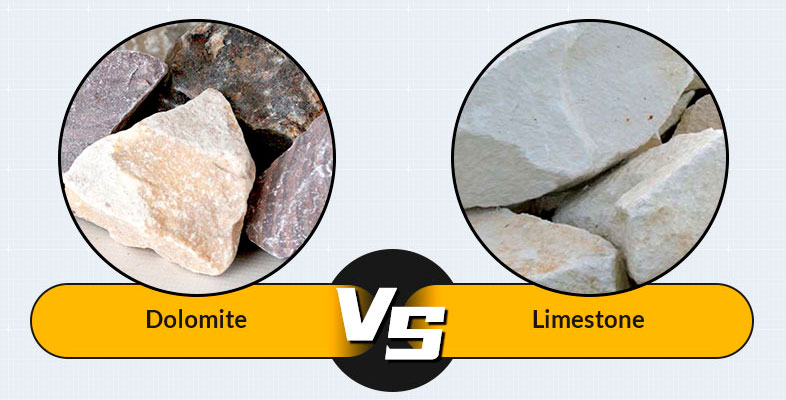

Dolomite: The color and texture are rich and colorful, with a glassy luster. In addition to white, there are also gray, transparent, green, brown, dark pink, etc.
Limestone: The color is relatively single, mainly gray or gray-black, and there are other colors such as yellow-brown, blood red, sea green, etc. The texture is relatively simple, there may be some small spots and stripes, the appearance is mostly opaque, and the texture is relatively soft.
Different chemical composition

Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) is mainly composed of calcium carbonate and silicate, and is a metamorphic rock. It contains more impurities, such as manganese, iron, quartz, etc. It is relatively soft and brittle, with more pores and cracks.

Limestone (CaCO₃) is mainly composed of calcium carbonate and is a sedimentary rock. It contains a small amount of magnesium, iron and other substances, and has a relatively hard texture, generally without cracks and pores.
Different physical properties
Dolomite: Relative to limestone, it has a higher density and specific gravity, and is not easily soluble in water. It is soluble in hot hydrochloric acid, but not soluble in 10% dilute hydrochloric acid.
Limestone: The composition and formation conditions directly affect the density and hardness. It will foam violently when exposed to cold dilute hydrochloric acid. It is softer than dolomite and has a smaller specific gravity.
Different applications
Dolomite uses

Building materials: It has a very rich color and is often used to produce new decorative materials such as glass, floor tiles, wall tiles and panels.
Ceramic industry: It can be used as a substitute for talc and calcite to reduce the firing temperature and improve the transparency of the body.
Refractory materials: Due to its stability and heat resistance, dolomite is often used to manufacture thermal equipment such as open-hearth furnaces and steelmaking converter linings.
Chemical industry: It is the main raw material for the manufacture of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizers and magnesium sulfate
Agricultural industry: Dolomite powder is a raw material for the manufacture of fertilizers and soil improvement.
Environmental protection: It has a good control effect on heavy metal pollution, phosphorus pollution, boron pollution, etc.
Uses of limestone

Building decoration: Limestone has a low hardness and is easy to process. It is the main raw material for making exterior walls, floors, columns, etc. in the construction industry. Generally, quicklime turns into slaked lime when it meets water, which is the raw material for brick and tile adhesives and coating materials.
Cement production: Limestone is the main raw material for making cement, which is of great significance to the stable development of the construction industry.
Iron and steel smelting: It can be used as a flux or slag-making material, playing an important role in the steel smelting process.
Chemical industry: It can be made into important calcium salts such as calcium chloride, calcium nitrate, and calcium sulfite through chemical processing.
Different crushing processes
Dolomite grinding process
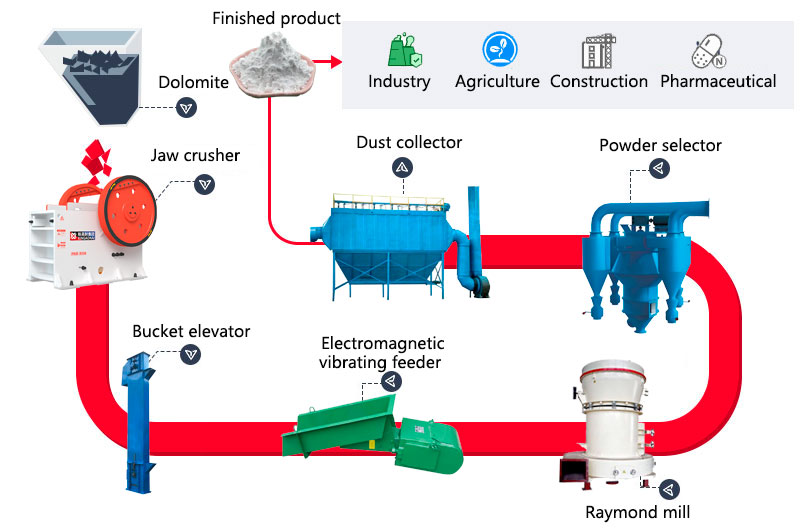
Required equipment: jaw crusher, Raymond mill, electromagnetic vibrating feeder, bucket elevator, etc.
Process flow: The dolomite material is sent to the jaw crusher through an electromagnetic vibrating feeder for coarse crushing; the dolomite that meets the particle size requirements enters the Raymond mill for grinding through a bucket elevator and an electromagnetic vibrating feeder; the dolomite that does not meet the particle size requirements enters the jaw crusher for crushing, until all the dolomite materials pass through the Raymond mill and meet the particle size requirements of the finished product.
Limestone grinding process

Required equipment: jaw crusher, impact crusher, conveyor, vibrating feeder, screening machine, limestone grinding machine, etc.
Process flow: The material is evenly sent to the jaw crusher by the vibrating feeder for crushing. When the raw material meets the grinding particle size requirements, it is sent to the silo by the bucket elevator. The electromagnetic vibrating feeder sends the raw material in the silo to the Raymond mill for grinding. After grinding, the blower sends it to the Raymond analyzer for screening. The powder that meets the requirements will follow the air flow and enter the large cyclone collector for collection. If it does not meet the requirements, it will continue to return to grinding until it is qualified. Finally, it is discharged through the powder discharge pipe.(xingaonai) Report this page